CS501 Mcqs
Quiz 1 Lec 1-9
#Mid-Term
WITH PROVE ANSWER
Important NOTE:-
Like share and comment too ..ager koi mistake hogaye ho to sorry and comment main lazmi mention krdijiye ga takey main correction krlon file main …. And like zaroor krein is hamein or bhe apsab keyliye files makes krny ke himat milti hey …JAZAKALLAH
All of the given are examples of register-to-memory data
transfer instructions except ____________.
Id
In FALCON-A instruction format of TYPE-2 constants and
variable should be in the range of
-32 to
+31
A relative address is calculated by adding the displacement
to the contents of the __________ .
Program
Counter
In MC68000, only the last __________ bits of 32-bit program
counter (PC) register are used to store memory addresses.
The
last 24 bits of the 32-bit Program
The status register of the 68000 has ____ condition codes.
8
In a simple RISC computer, the size of each register is
___________.
32 bits
Almost every commercial computer has its own particular
__________ language.
Assembly
Language
Which one of the following circuit design levels is called
the gate level?
Circuit
Level
In Falcon-A ISA, which of the following opcodes is used to
perform "No Operation"?
No Operation" is 20
. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
store register relative (str) instruction?
(op<4..0>=4):M[rel]<-R[ra]……confirm
2. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
load displacement address (Ia) instruction?
(op<4..0>=5):R[ra]<-disp…….confirm
3. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
load relative address (Iar) instruction?
(op<4..0>=6):R[ra]<-rel……confirm
4. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
conditional branch (br) instruction?
(op<4..0>=8): (cond :
PC<- R[rb]),…..confirm
5. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
branch and bank (brl) instruction?
Cond : (PC <- R
[rb]))…..confirm
6. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
store register (st) instruction?
(op<4..0>=3):M[disp]<-R[ra]……confirm
7. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent load
register relative (Idr) instruction?
(op<4...0>=2) : R[ra]
<- M[rel]…..confirm
8. Which of the given RTL description is used to represent
load register (Id) instruction?
(op<4..0>=1):R[ra]<-M[disp]……confirm
9. In a simple RISC computer the size of each register is
_______.
32 bits…….confirm
10. A _________ is a device that provides a shared data path
to a number of devices that are connected to it.
Bus…….confirm
11. _________ instruction is used to load a register with an
immediate data value.
Ia……confirm
12. ___________ instruction is used to store register
contents to memory
St……confirm
13. _______ instruction is used to load register from memory
instruction
Id…….confirm
14. Which type of instructions load data from memory into
register or store data from register into memory and transfer into memory and transfer
data between different kinds of special-purpose registers?
Data transfer……confirm
15. In RTL, which of the following symbols is used to store
some data into a register?
:=……confirm
16. A stack based machine is also called _________.
0-address machine……confirm
17. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold the instruction register, used to hold the current instruction
The bits 31 through 0……confirm
18. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold program counter(it holds the memory address of next instruction to be
executed)?]
The bits 31 through 0……confirm
19. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold short displacement or immediate field?
The bits 16 through 0…..confirm
20. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold count or modifier field?
The bits 16 through 0…..confirm
21. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold an operand, an address index, or a branch target register?
The bits 21 through 17…..confirm
22. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold a second operand, conditional test, or a shift count register?
The bits 16 through
12……..confirm
23. Which of the following bits of SRC instruction are used
to hold long displacement field?
The bits 21 thorugh 0…..confirm
24. Which of the following is example of direct indirect
addressing mode?
M[[R5] + [R5]]…..confirm
25. Which of the following RTL description is used to
represent the target register of
Falcon-A instruction
Ra<2..0>:=IR<10..8>…..confirm
26. Which of the following RTL description is used to represent
the operation code of Falcon-A instruction
Op<4...0>:=
IR<15..11>:……confirm
27. Which of the following RTL description is used to represent
the operand or address index of Falcon-A instruction
Rb<2..0>:=IR<7..5>:…..confirm
28. Which of the following RTL description is used to represent
the second operand of Falcon-A instruction
Rc<2..0>:=IR<4..2>…..confirm
29. Which of the following RTL description is used to represent
the short displacement field of Falcon-A instruction
C1<4..0>:=IR<4..0>……confirm
30. Which of the following RTL description is used to represent
the long displacement or the immediate field of Falcon-A instruction
C2<7..0>:=IR<7..0>:…….confirm
31. The instruction Load R1, [R3 + 20] is an example of
which of the following addressing modes?
Register
32. In SRC, the op-code for NOP operation is _________.
0
33. Which of the following RTL description is used to
represent all general purpose register of SRC?
R[0..31]<31..0>;...confirm
34. To implement an N-bit barrel shifter in form of a combinational
circuit, we require N _______.
Multiplexers…..confirm
35. A general purpose digital computer has _______ main
components
4…..confirm
36. __________ instruction is used to divide a register value
by the immediate value in FALCON-E processor
divi…..confirm
37. __________ instruction is used to push the contents of a
specified general purpose register to the stack in FALCON-E processor
Push……confirm
38. __________ instruction is used to pop the value that is
at the top of the stack in FALCON-E processor
Pop…..confirm
39. _________instruction is used to load a register with
memory contents using displacement addressing mode in FALCON-E processor
Idr…..confirm
40. __________ instruction is used to store a register value
into memory using displacement addressing mode in FALCON-E processor
Str…..confirm
41. __________ instruction is used to branch if source operand
is less than target address in FALCON-E processor
Bl……confirm
42. __________ instruction is used to branch if source
operand is greater than target address in FALCON-E processor
Bg……confirm
43. __________ instruction is used to multiply an immediate
value with a value stored in a register in FALCON-E processor
Muli……confirm
44. __________ instruction is used to evaluate logical
exclusive or in FALCON-E processor
Xor, xori…..confirm
45. Which of the following measure can be best used for
calculating the performance of computation intensive application
MFLOPS……confirm
46. All of the below given processors employ Little-Endian
storage format except_____.
Falcon-A……confirm
47. The instruction shifti R1, R2, 20 is an example of which
of the following addressing modes?
Immediate…..confirm
An ________ is a program that takes basic computer instructions and converts them into a pattern of bits that the computer's processor can use to perform its basic operations.
Assembler
The multiplexer is used to decide which value is transferred to be written
back to the register file.
MP2
MP3
MP4
MP5
Which of the following condition
is evaluated when executing the branch instruction “brzr R2, R1”?
If(R2==0)
If( R1 >0 )
If( R1==0)
If( R1 < 0)
In case of SRC processor, bits of IR (instruction register) are reserved for the opcode.
0 to 4
11 to 15
27 to 31
59 to 63
Which of the given RTL description is used to represent “load instruction register”
(ldr) instruction?
(op<4..0>=6): R[ra] rel
(op<4..0>=2): R[ra] M [rel]
(op<4..0>=2): M[disp] R [ra]
(op<4..0>=2): M[rel] R [ra]
Instruction is
used to divide a register
value by immediate value in FALCON-E
processor.
div
idiv
divi
divim
Which field of machine language
instruction is the “type of operation” that is to be performed.
Op-code(or the operation code)
CPU register
Memory Cells
I/O Location
Which of the following control signal is NOT activated
during instruction fetch operation?
PCout
LC
LMAR
Cout
In case of FALCON-A instruction
are present which are not present in SRC processor.
create and destroy
in and out
open and close
read and write
provides a temporary
storage for the address of memory location
to be accessed.
MAR
Which of the following register
is used to enable the tri-stable buffers with the MBR?
MBRout
MARout
LMBR
INC4
What functionality is performed by the instruction “str R8, 34” of SRC?
It will load the register
R8 with the contents
of the memory location M[PC+34]
It will load the register
R8 with the contents of the memory
location M[34]
It will store the register R8 contents
to the memory location M[PC+34]
It will store the register
R8 contents to the memory
location M[34]
Program Counter(PC) holds the
memory address of:
Previous Instruction
Current Instruction
Next Instruction
Previous and Current
Instruction
What is the working
of Processor Status
Word (PSW)?
To hold the current status
of the processor
To hold the current
address of the process
To hold the instruction that the computer
is currently processing
To hold the address of the next instruction in memory that is to be executed
mul is the example of a(n) operation.
Logic
Shift
Arithmetic
Data transfer
Control Signal for RTL “IR< ---MBR” will be---------
MBRout,LIR
PC< --C
PC< --MBR
PC< --IR
What does the instruction”ldr R3, 58” of SRC do?
It will load the register
R3 with the contents
of the memory location M[PC+58]
It will load the register R3 with the relative address itself(PC+58)
It will store
register R3 contents to the memory location
M[PC+58]
It will store the value of register
R3 at the relative address itself(PC+58)
The status
register of the 68000 has condition codes.
2
3
5
8
Which of the instruction is used to load register
from memory using relative address?
ld instruction
ldr instruction
lar instruction
str instruction
For the type instruction, we require a register to hold the data that is
to be loaded from the memory, or
stored back to the memory.
Jump
Control
L
load/store
Branch
In a processor, is responsible for the synchronization of internal as well external
events.
Memory Unit
Data Unit
Arithmetic & Logic Unit
Control Unit
In CPU design, creates or forms the interface between
the data path and control
unit.
Buses
ALU
Control signal
cache
Control signal enables the input to the PC for receiving a value that is
currently on the internal
processor bus.
LPC
INC4
LC
Cout
In SRC, the effective address is computed a run-time
by adding a constant to value of register.
FLAGS
IR
PC
Ra
control signal allow the
content of the program
counter register to be written onto the internal processor
bus.
INC4
LPC
PCout
LC
In instruction format of EAGLE processor, there is no field reserved
for the operands.
Type V
Type Y
Type X
Type Z
In Type C instruction
of SRC, bits are allocated
for constant values.
16
17
21
22
A general purpose
digital computer has main components.
2
3
4
5
The instruction will load the register R3 with the contents
of the memory location M[PC+56].
lar R3,M[56]
ldr R3,M[56]
ldr R3,56
lr R3,[56]
In FALCON-A
instruction format of Type-2 constants and variable should be in the range of.
-132 to +131
-164 to + 163
-32 to + 31
-128 to + 127
In a FALCON-A
assembly program, labels are used to implement jump.
Direct
Indirect
Relative
Displacement
In “Jump [8]” instruction, the size of the constant
fields is bits.
4
5
8
16
The multiplexer is used to decide which value is transferred to be written
back to the register file.
MP2
MP3
MP3
MP5
is a register
which takes input from the ALSU as memory address
to be accessed and transfer the
memory contents on that location
onto the memory
sub-system.
PC
MBR
MAR
IR
In pipe-lined processor, there should be a port
register file so that if the register
write and register
read
stages overlap they can be performed in parallel.
Four
Three
Two
One
Which of the following registers is used as an implicit operand
in MUL/DIV instruction of FALCON-A?
R0
PC
IR
SP
Which one of the following control signals
causes the data from the bus to
be read into the register
MAR.
MARout
MARin
LMAR
None of the given
Which of the following operations is NOT performed by using miscellaneous instruction?
Clearing all registers
Stopping the processor
NOP
Returning from a procedure
To set the value of micro-PC from branch address, the value of 4 to 1 multiplexer is------------
00
01
10
11
The instruction “PUSH A”
is an example of ------------
0-address instruction
1-address instruction
2-address instruction
3-address instruction
Which of the following branch
instruction has a condition which is always
executed?
JZ
JUMP
JPL
JMI
hazard occurs when attempting to access same resource in different ways at the same time.
Branch
Data
Structural
Instruction
is an example
of Miscellaneous instruction.
Shift
Store
Halt
Call
Which type of instructions enables
mathematical computations?
Arithmetic
Control
Data transfer
Numeric
VLIW Stands
for-------------
Variable Length Instruction Word
Very Long Instruction Word
Very Long Instruction Width
Variable Length Instruction Width
Which of the following is NOT related
to the architecture of the computer?
Instruction set
Control signal
I/O mechanism
Memory addressing modules
In SRC, the general-purpose register
file includes registers, each 32 bit wide.
6 Registers R0 to R15
24 Registers R0 to R23
32 Registers R0 to R31
64 Registers R0 to R63
Which of the following RTL description is used for specifying the operation of an SRC instruction?
IR<31..27>
IR<22..26>
IR<21..17>
IR<21..0>
What is the size of the memory space that is available to FALCON-A processor?
2^8 bytes
2^16 bytes
2^32 bytes
2^64 bytes
How can we refer to an instruction register (IR), of 16 bits (numbered 0 to 15) using RTL.
IR<16..0>
IR<15..0>
IR<16..1>
IR<15..1>
What is the working
of Processor Status Word (PSW)?
To hold the current
status of the processor.
To hold the address
of the current process
To hold the instruction that the computer
is currently processing
To hold the address
of the next instruction in memory that is to be executed
What does the instruction “ldr R3, 58” of SRC do?
It will load the register R3 with the contents of the memory
location M [PC+58]
It will load the
register R3 with the relative
address itself (PC+58).
It will store the register
R3 contents to the memory
location M [PC+58]
No operation
What is the instruction
length of the FALCON-E processor?
8 bits
16 bits
32 bits
64 bits
Which one of the following
portions of an instruction represents the operation to be performed?
Address
Instruction code
Opcode
Operand
Which one of the following
is the highest level of abstraction in digital design in which the computer
architect views the system
for the description of system components and their interconnections?
Processor-Memory-Switch level (PMS level)
Instruction Set
Level
Register Transfer Level
None of the given
Identify the opcode,
destination register (DR),
source registers (SA and SB i/e source
register A and source register B) from the following
example. ADD R1, R2, R3
Opcode= R1, DR=ADD,
SA=R2, SB=R3
Opcode= ADD, DR=R1,
SA=R2, SB=R3
Opcode= R2, DR=ADD,
SA=R1, SB=R3
Opcode= ADD, DR=R3, SA=R2, SB=R1
Which one of the following
circuit design levels is called
the gate level?
Logic Design
Level
Circuit Level
Mask Level
The CPU includes
three types of instructions, which have different
operands and will need different representations. Which one of the instructions
requires two source registers?
Jump and branch format instructions
Immediate format instructions
Register format
instructions
All of the above
P: R3 <- R5 MAR <- IR These two are instructions
written using RTL .If these two operations is to occur simultaneously then which
symbol will we use to separate them so
that it becomes a correct statement with the condition that two operations occur
simultaneously?
Parentheses ()
Arrow <-
Colon :
Comma ,
In which of the following instructions the data move between
a register in the processor and a memory
location (or another register) and are also called
data movement?
Arithmetic/logic
Load/store
Test/branch
None of the given
Which one of the following is the highest level of
abstraction in digital design in which the computer architect views the system for the description of system components and their interconnections?
Processor-Memory-Switch level (PMS level)
Instruction Set
Level
Register Transfer Level
None of the given
Identify the opcode,
destination register (DR), source registers (SA and SB i/e source register
A and source register B) from the following
example. ADD R1, R2, R3
Opcode= R1, DR=ADD,
SA=R2, SB=R3
Opcode= ADD, DR=R1,
SA=R2, SB=R3
Opcode= R2, DR=ADD,
SA=R1, SB=R3
Opcode= ADD, DR=R3, SA=R2,
SB=R1
Which one of the following
circuit design levels
is called the gate level?
Logic Design
Level
Circuit Level
Mask Level
None of the given
The CPU includes
three types of instructions, which have different
operands and will need different representations. Which one of the instructions
requires two source registers?
Jump and branch format instructions
Immediate format instructions
Register format
instructions
All of the above
P: R3 <- R5 MAR <- IR These two are instructions
written using RTL .If these two operations is to occur simultaneously then which symbol will we use to separate them so
that it becomes a correct statement with the
condition that two operations occur simultaneously?
Parentheses ()
Arrow <-
Colon :
Comma ,
In which of the following
instructions the data move between a register in the processor and a memory
location (or another
register) and are also
called data movement?
Arithmetic/logic
Load/store
Test/branch
None of the given
What does the word ‘D’ in the ‘D-flip-Flop’ stands for?
Data
Digital
Dynamic
Double
The instruction will load the register R3 with the contents
of the memory location M [PC+56]
Add R3, 56
lar R3, 56
ldr R3, 56
str R3, 56
What is the instruction length of the
FALCON-E processor?
8 bits
16 bits
32 bits
Which one of the following are the code size and the
Number of memory bytes respectively for a 2-address instruction?
4 bytes, 7 bytes
7 bytes, 16 bytes
10 bytes, 19 bytes
13 bytes, 22 bytes
Which one of the following portions of an instruction represents the operation to be performed?
Address
Instruction code
Opcode
Operand
Which operator is used to ‘name’ registers, or part of registers, in the Register
Transfer Language?
:=
&
%
©
What is the size of the
memory space that is available to FALCON-A processor?
2^8 bytes
2^16 bytes
2^32 bytes
2^64 bytes
An “assembler”
that runs on one processor
and translates an assembly language
program written for another processor into the machine language
of the other processor is called a ----------------
compiler
cross assembler
debugger
linker
Which instruction is used to store register
to memory using relative address.
ld instruction
ldr instruction
lar instruction
str instruction
Which of the following can be defined as an address of the operand in a computer type instruction or the target address in a branch type instruction?
Base address
Binary address
Effective address
All of the given
How can we refer to an instruction register (IR), of 16 bits (numbered 0 to 15) using RTL?
IR<16..0>
IR<15..0>
IR<16..1>
IR<15..1>
What functionality is performed by the instruction “str R8, 34” of SRC?
It will load the register R8 with the contents of the memory
location M [PC+34]
It will load the register
R8 with the relative address itself (PC+34).
It will store the register
R8 contents to the memory
location M [PC+34]
No operation
Which type of instructions help in changing
the flow of the program
as and when required?
Arithmetic
Control
Data transfer
Floating point
Which of the following statements is/are true about RISC
processors’ claimed advantages over CISC processors?
(a) Keeping regularly accessed variables in registers as opposed to keeping
them in memory facilitates faster
execution. (b) RISC CPUs outperform CISC CPU’s in procedural programming environments. (c) Instruction pipelining has helped RISC CPU’s to attain
a target of 1 cycle per instruction.
It is easier to maintain the “family concept”
in RISC CPU.
(a), (b) &(c)
(b), (c) &
(e)
(c), (d) &
(e)
(a), (c) & (d)
Which one of the following
is the highest level of abstraction in digital design in which the computer
architect views the system
for the description of system components and their interconnections?
Processor-Memory-Switch level (PMS level)
Instruction Set
Level
Register Transfer Level
None of the given
Which one of the following
is/are the features
of Register Transfer
Language? a) It is a symbolic
language
It is describing the internal organization of digital computers c) It is an elementary operation performed (during
one clock pulse),
on the information stored in one or more registers d) It is high
level language.
(b) only
& (b) only
,(b) & (d)
(b),(c) & (d)
CISC
RISC
SRC
FALCON
Which one of the following
registers holds the instruction that is being executed?
Accumulator
Address Mask
Instruction Register
Program Counter
For any of the instructions that are a part of
the instruction set of the SRC, there are certain _ required; which may be used to select the appropriate function
for the ALU to be performed, to select the appropriate registers, or the appropriate memory location.
Registers
Control signals
Memory
None of the given
The external interface
of FALCON-A consists of a data bus.
8-bit
16-bit
24-bit
32-bit
In which one of the following techniques, the time a processor spends
waiting for instructions to be fetched
from memory is minimize
Perfecting
Pipelining
Superscalar operation
Speedup
enable the input to the PC for receiving a value that is currently on the internal
processor bus.
LPC
INC4
LC
Cout
The processor must have a way of saving information about
its state or context so that it can be restored upon return from the -------------
Exception
Function
Thread
Stack
is the ability
of application software
to operate on models
of equipment newer than the model for
which it was originally developed.
Backward compatibility
Data migration
Reverse engineering
Upward compatibility
control signal
allows the contents
of the Program Counter register
to be written onto the
internal processor bus.
INC4
LPC
PCout
LC
Which one of the following registers stores a previously calculated value or a value loaded from the main
memory?
Accumulator
Address Mask
Instruction Register
Program Counter
Computer system performance is usually measured
by the ---------------
Time to execute
a program or program mix
The speed with which it executes programs
Processor’s utilization in solving the problems
Instructions that can be carried out simultaneously
The external interface
of FALCON-A consists of a address bus.
8-bit
16-bit
24-bit
32-bit
Which one of the following
register(s) that is/are programmer invisible
and is/are required
to hold an operand or result value while the bus
is busy transmitting some other value?
Instruction Register
Memory address register
Memory Buffer Register
Registers A and C
The external interface
of FALCON-A consists of a address
bus and a data bus.
8-bit , 8-bit
16-bit , 16-bit
16-bit , 24-bit
16-bit , 32-bit
is the ability
of application software
to operate on models
of equipment newer than the model for
which it was originally developed.
Backward compatibility
Data migration
Reverse engineering
Upward compatibility
Which one of the following
registers stores a previously calculated value or a value loaded from the main
memory?
Accumulator
Address Mask
Instruction Register
Program Counter
Which one of the following
register(s) contain(s) the address
of the place the CPU wants
to work with in
the main memory and is/are directly connected
to the RAM chips on the motherboard?
Instruction Register
Memory address
register
Memory Buffer Register
Registers A and C
FALCON-A processor bus has
16 lines or is 16-bits
wide while that of SRC is wide.
8-bits
16-bits
32-bits
64-bits
enable the input to the PC for receiving a value that is currently on the internal
processor bus.
LPC
INC4
LC
Cout
The external interface
of FALCON-A consists of a data bus.
8-bit
16-bit
24-bit
32-bit
For any of the instructions that are a part of the instruction
set of the SRC, there are certain
required; which may be used
to select the appropriate function for the ALU to be performed, to select
appropriate registers, or the appropriate memory location
Registers
Control signals
Memory
None of the given
Among the two approaches
available to design a control
unit, hardware approach
is relatively----------
as compared to micro-programming.
Slow
Fast
Average
Better
The MAR is connected directly
to the-----------
MBR
CPU Internal bus
CPU external bus
LIC
Which of the following is not a part of processor state?
IR
PC
Stacks
Registers
form the branch control field in the micro instruction.
C Bits
M Bits
B BITS
M Bits
During the RESET operation of processor, control
step counter is set to --.
1
0
2
-1
An “assembler” that runs on one processor
and translates an assembly language
program written for another processor into the machine language
of the other processor is called
a------------
Compiler
Cross assembler
Debugger
linker
In FALCON-A processor, the size of each I/O port is---------------
16 bits
8 bits
8 bytes
256 bytes
is defined as the number
of instructions processed
per second.
Memory access
Throughput
ALU operation
Latency
In FALCON-A ISA, which of the following opcodes is used to perform
“No Operation”?
20
21
22
23
is an example
of Miscellaneous instruction:
Shift
Store
Halt
Cell
To apply two shifts
to an
input number using
the barrel shifter,
the control signals S1 and S0 of the shifter
should be .
S1 = 1 and S0 = 1
S1 = 0 and S0 = 1
S1 = 1 and S0 = 0
S1 = 2 and S0 = 0
Which one of the followings is the correct RTL description for sign extensions of an 8-bit constant:
(8aIR<7>©IR<7..0>)
(8aIR<5>©IR<8..0>
(8aIR<7>©IR<6..0>
(8aIR<8>©IR<7..0>
In MC68000, register is used as stack pointer:
A0
A7
D0
D7
In which of the following instructions, the data moves
between a register in the processor and a memory
location:
Arithmetic
Load/ Store
Branch
Logic
The size of data bus of
mc68000 processor is:
8 bits
16 bits
20 bits
32 bits
Which one of the following
operations is NOT performed
by using miscellaneous instructions?
Clearing all registers
Stopping the processor
NOP
Returning from a procedure
In case of FALCON-A instructions are present which are not present
in the SRC processor:
Create and destroy
In and out
Open and close
Read and write
In Type C instruction of SRC , bits are allocated
for content value:
16
17
21
22
RISC stands for?
Registers internal system cache
Reduced instruction set computer
Registers instruction set computer
Reduced internal system
computers
Which of the followings
is not an example of super-scalar processors?
PowerPC601
IAPX88
Intel P6
DEC Alpha 21164
In EAGLE processor, which of the following notations is used to represent a memory word stored at address 8?
M [8]
<0..15>:= M[8]©M[9]
M[8]<15..0>:=M[9] ©M[8]
M[8]<15..0:=M[8] ©M[9]
M[8]<0..15>:=M[9] ©M[8]
form the branch address field in the micro instruction:
C bits
M bits
B bits
A bits
What does the instruction “idr R3, 58” of SRC
do?
It will load register
R3 with the contents of the memory location M[PC+58]
It will load register R3 with
the relative address itself (PC+58)
It will store register R3 contents to the memory location M[PC+58]
It will store the value of register
R3 at the relative address itself (PC+58)
The SPARC architecture defines a that allows for multiple address spaces.
Memory Location Unit(MLU)
Memory Mapping Unit( MMU)
Memory Shifting
Unit (MSU)
Memory Arithmetic Unit (MAU)
For a processor having 32 general purpose
register, bits are required for each register
field in the
instruction:
32
3
8
5
Which of the following registers
is/are programmer invisible
and is/are required
to hold an operand or result value
while the bus is busy transmitting some other value?
Instruction register
Memory address
register
Memory Buffer Register
Registers A and C
In SRC which of the following is a notation which is used to
repeat 32- bit memory word stored at address
starting from 56?
M[56]<31..0>:=M[56]M[57]M[58]M[59]
M[56]<0..31>:=M[56]M[57]M[58]M[59]
M[56]<0..31>:=M[59]M[58]M[57]M[56]
M[56]<0..31>:=M[59]M[58]M[57]M[56]
·
Which of the following branch
instruction has a condition which is always
executed?
JZ
JUMP
JPL
JMI
Which of the following EAGLE instruction is used to initialize
all the registers by setting
them to 0?
NOP
HALT
INIT
RESET
Which notation do we use to name different fields
of a register in RTL?
0
<=
· +
:=
Which of the following instruction is considered most important in pipelined EAGLE architecture?
HALT
NOP
INIT
RESET
SPARC uses a simple
set of instruction format.
64-bit
12-bit
16-bit
32-bit
The ALSU function
“INC2” increments the by 2 and the output is stored in the buffer
register.
PC,A
IR,A
PC,C
IR,C
Which temporary register
is loaded with either a register value from the register file or a constant from the instruction?
Y3
X3
Z4
Z5
“Finite-state machine” concepts are usually used to represent
the control unit where
every state corresponds to clock cycles(s).
1
2
4
16
Total number of data registers in Motorola 68000 processor are----------
8
12
24
32
instruction is used to load a register
with an immediate value.
la
lar
ld
ldr
A computer belongs to which of the following subset of the systems?
Mechanical system
Electrical system
Optical system
Magnetic system
In FALCON-A
processor , the size of each I/O
port is-------------
16 bit
8 bit
8 bytes
256 bytes
Type A of SRC has which of the following instruction?
andi, instruction
No operation or nop instruction
lar instruction
ldr instruction
Stop operation or stop instruction
(a)&(b)
(b)&(c)
(a)&(e)
(b)&(e)
In which of the following
technique, the time a processor
spends waiting for instruction to be
fetched from memory is minimized?
Perfecting
Pipelining
Super-scalar operation
Speed up is the ability
of application software
to operate on models
of equipment near than the model for which it originally developed.
Backward compatibility
Data migration
Reverse engineering
Upward compatibility
Which of the following register
stores a previously calculated value or a value loaded from the main memory?
Accumulator
Address Mask
Program counter
Computer system performance is usually measured
by the ----------
Time to execute a program or program mix
The speed in which it executes programs
Processor’s utilization in solving the problems
Instructions that can be carried
out simultaneously
Which of the following code size and the number
of memory bytes respectively for a 2-address instruction.
4 bytes, 7 bytes
7 bytes ,16 bytes
10 bytes , 19 bytes
13 bytes, 19 bytes
Which of the the given below measures is/are
used for comparison of performance of various machine?
Execution time
MFLOPS
MIPS
All of the given
There are type of RESET operation in SRC.
Three
Four
Two
five
Type checking
allows the to determine memory for variables.
Compiler
Debugger
Linker
loader
In FALCON-A
processor, memory word size is----------------
1 byte
4 bytes
8 bytes
2 bytes
What functionality is performed by the by the instruction “lar R3, 36” performed.
It will load the register
R3 with the contents of memory location
M[PC+36]
It will load the register
R3 with the relative address
itself (PC+36)
It will store
the register R3 contents of memory location
M[PC+36]
It will left rotate the value of R3 36 times and will store the value in R3
In which one of the following addressing modes, the operand does not specify an address but it is the actual data to be used.
Immediate
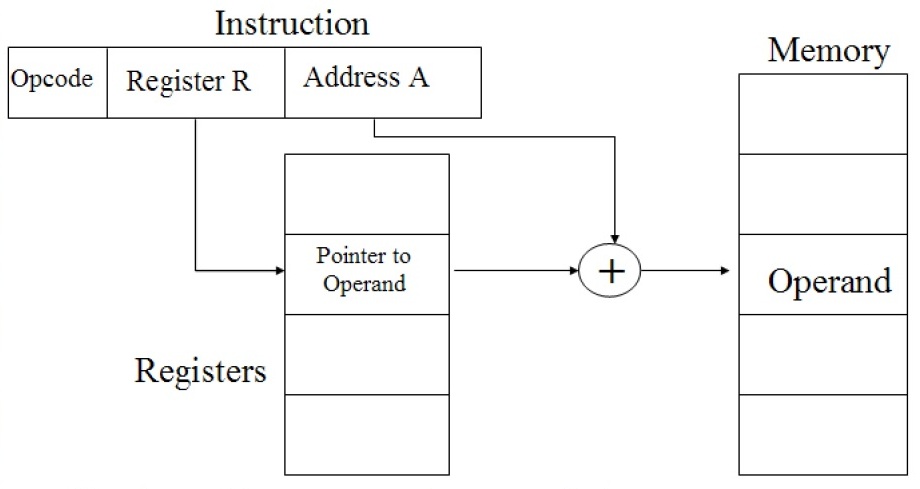
In this figure, the constant value specified by the immediate field is added to the register value, and the resultant is the index of memory location that is referred i.e. Effective Address = A + (content of R) . Identify the addressing mode.
Displacement
In ________ address mode, the actual data is stored in the instruction.
Immediate
Which one of the following registers store a previously calculated value or a value loaded from the main memory?
Accumulator
Which field of the machine language instruction is the “type of operation” that is to be performed?
Op-code
An instruction that specifies one operand in memory and one operand in a register would be known as a ________ address instruction.
1-1/2
Which one of the following instructions is used to load register from memory using a relative address?
ldr
Which one of the following is an address (binary bit pattern) issued by CPU?
Effective
The instruction ________ will load the register R3 with the contenets of the m\emory location M [PC+56]
ldr R3, 56
Which instruction is used to store register to memory using relative address?
str instruction
Type A of SRC has which of the following instructions?
- andi, instruction
- No operation or nop instruction
- lar instruction
- ldr instruction
- Stop operation or stop instruction
- 1 & 2
- 2 & 3
- 3 & 5
- 2 & 5




Thanks everone